A study aiming to provide a comprehensive understanding of the opportunities for AI in banking, financial services and insurance in 2024. We have analysed the impact AI will have on every function and every activity performed by banks, insurers, FinTechs and other financial services.
Fifty One Degrees is an AI Consultant that advises financial services and insurance firms on adopting Generative AI to create a competitive advantage. Generative AI can ingest vast volumes of natural language documentation, such as policies, procedures, regulations and corporate documentation, and then give accurate insights, responses or automation based on the documentation. The result is serving customers better and enabling dramatic resource efficiencies.
The authors of this study are Nick Harding and Mark Somers, who are the CEO and CPO of Fifty One Degrees. Before Fifty One Degrees, Nick co-founded and led Fluro, one of the fastest-growing FinTechs in the UK. Whereas, Mark co-founded and led 4most, the UK’s largest independent credit and analytics consultancy, which served the global financial services industry.
The advent of artificial intelligence (AI) has ushered in a new era of possibility, disrupting industries and redefining the way we interact with technology. In recent years, one facet of AI has captured the global imagination: Generative AI. This technology is capable of ingesting huge volumes of information, documentation and policies, then accurately providing insights and answering questions based on that information instantly, therefore offering transformation to various sectors, with the financial services and insurance industries being particularly appropriate.
Generative AI’s potential to redefine what’s possible for financial services and insurance processes has not gone unnoticed by thought leaders across academia, government, and industry.
“Generative AI holds the key to unlocking unprecedented levels of efficiency, personalisation, and decision-making within the financial sector,” contends a recent report from the University of Oxford(1).
McKinsey echoes this sentiment, predicting that the adoption of generative AI could streamline operations, boost client satisfaction, and ultimately drive greater profitability within these sectors.
“Insurance companies embracing generative AI are likely to have a significant competitive edge in a market driven by innovation and customer experience.” Oliver Wyman(2) recently commented.
“The ability of generative AI to automate routine tasks, optimise processes, and provide valuable insights will be a decisive factor in shaping the future of the UK’s financial industries,” remarked a spokesperson from the UK’s Office for Artificial Intelligence.
This study aims to provide a comprehensive and nuanced understanding of the opportunities that lie ahead for AI in banking, financial services and insurance in 2024. By analysing the impact AI will have on every function and every activity performed by typical mainstream firms, this study delves deeply into the multifaceted applications of AI in this sector. The study includes analysis of over 300 internal and external tasks and activities spanning fourteen functions; Analytics and Data Science, Collections, Compliance, Credit & Enterprise Risk, Customer Services, Finance & Treasury, Human Resources, Leadership, Legal, Marketing, Product, Sales, Technology and Underwriting. It aims to define the transformative potential of the technologies that are already on the market, and the likely impact on industry practices, customer experiences, efficiencies and financial impact.
Off-the-shelf AI technologies, such as Microsoft Copilot and Google Gemini have not been included in the findings of this study. However, it is expected these standard tools will further improve the efficiency and quality of work.
Of the 311 activities spanning the fourteen key functions in financial services firms, 85% of activities would either be made more efficient or the quality improved by AI technology being deployed. More than 8 in 10 activities will see efficiency improvements, whereas just over half will see quality improvements.
Assistants supporting team members with one or more specific functions (called ‘Team Assistants’ in this study) will benefit 75% of tasks undertaken by financial services and insurance firms. Team member assistants are built using Generative AI models, and trained on specific policies, procedures and regulations and they impact functions within the financial institution where large volumes of unstructured data and information (for example, documentation) are processed, such as Compliance, Legal and Underwriting. In some cases, these AI assistants will make employees more efficient, whereas in other places they will automate some of the work currently performed by employees altogether.
Other AI tools, which are also often powered by Generative AI will be the next most impactful, creating gains in 39% of activities. Examples of Other AI tools include AI-powered training, AI-based legal tools, AI finance tools, and many more.
Traditional machine learning techniques (called ‘ML Models’ in this study), which have been used successfully for almost a decade already, can positively impact 25% of tasks. ML Models are not new technologies but are very powerful when combining various sources of numeric information into rankings, for example, which customer should a collections team member call next, or which customers should be approved for a loan.
Assistants supporting customer enquiries (called ‘Customer Assistants’ in this study) impact the least number of activities, at 11%. However, when observing at a function level, as opposed to over the complete organisation, Customer Assistants transform the quality and efficiency of customer-facing divisions such as customer services and underwriting functions.
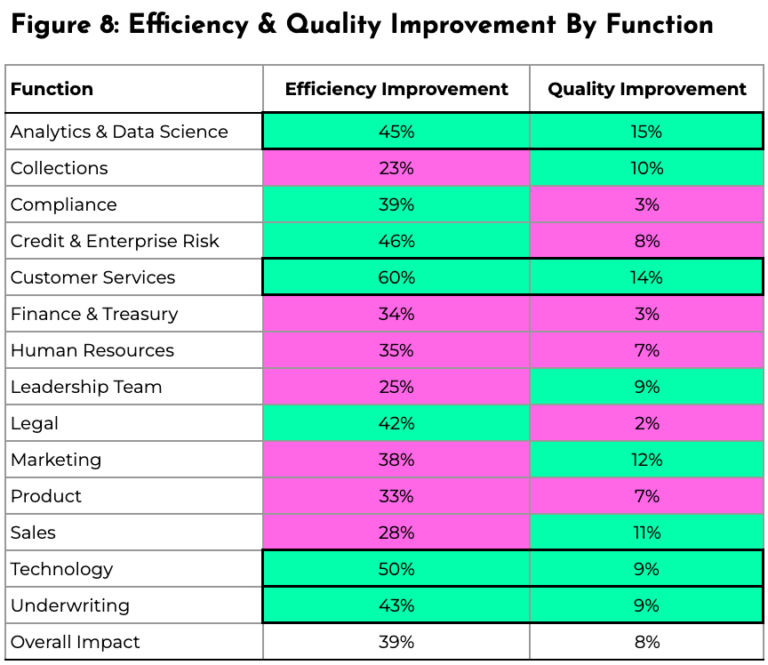
Our analysis shows that several functions within financial services firms can both increase efficiency and the quality of work delivered through the use of AI. Functions that will benefit more than the average from both positive characteristics are Analytics & Data Science, Technology, Customer Services and Underwriting. Other functions will benefit more than average from just one of the qualities, for example, Compliance, Credit & Enterprise Risk and Legal will experience greater efficiency impact than the average, however, in these functions, the quality of work is unlikely to increase at the same rate.
This study comprises the analysis of 311 tasks and activities performed in financial services and insurance companies, combined with a range of other sources of information. Each of these activities was analysed to understand whether it is an internally or externally focused task, how intensive the activity is, which AI technologies available in February 2024 might improve the efficiency or quality of that task, and by how much.
The impact across a complete financial institution is significant, with 85% or 263 activities expected to become more efficient or work generated to be of higher quality.
No Data Found
The tasks that will be most impacted by the AI technology currently on the market are the least intensive tasks, that are often repetitive and performed in high volumes, such as processing customer applications, customer enquiries, quality assurance or many others.
No Data Found
Overall, it will be the internally focused tasks that see the greatest efficiency gains in 2024, rather than externally focused tasks such as interacting with customers. In part, this is driven by caution over externally facing activities where customer outcomes are being impacted. The average across functions shows that 41% of internally focused tasks will become more efficient, whereas 34% of external activities will benefit.
No Data Found
The majority of tasks performed by financial institutions can become more efficient by using AI technologies, with 84% of tasks benefiting.
No Data Found
When split by function and impact, this study finds that most tasks will have a low or moderate impact on the technology that is currently available. Therefore this analysis highlights that AI will not replace human work in 2024, but rather increase the volume of tasks performed per capita. Only 17% of tasks will be highly automated with current AI technology.
Loading..........
The Data is Not Available
The quality of the work being undertaken will still be boosted in 51% of tasks. Analysed in isolation this figure is desirable for a financial institution, but when compared with the efficiency gains above it is clear that the greatest impact in 2024 will be on efficiency.
No Data Found
The scale of the impact on quality is also skewed lower, with approximately 80% of tasks having no or low-quality gains from AI services.
Loading..........
The Data is Not Available
When combined it becomes clear that some functions will benefit in terms of efficiency and quality. Analytics & Data Science, Technology, Customer Services and Underwriting all benefit in both measures, whereas, Compliance, Credit & Enterprise Risk and Legal will experience greater efficiency impact than the average. When considering an AI adoption roadmap, it would be most effective to focus on the functions benefiting both measures first.
Internally focused assistants supporting team members with their work (Team Assistants) are the most impactful use of AI technology in 2024. These assistants are built using generative AI and can be bespoke, supporting specific functions with specific knowledge.
No Data Found
When exploring deeper on the same analysis it becomes clear how the application of AI technologies will transform functions differently. Team member assistants will impact functions where large volumes of documentation, policy, regulation, agreements and other natural language information are processed. By their nature, customer assistants can only provide gains where customer interactions occur. ML Models are not new technologies but are very powerful when combining various sources of numeric information into rankings, for example, which customer should a collections team member call next, or which customers should be approved for a loan. And finally, Other AI tools, which are often powered by Generative AI models, are being applied to almost every function across every industry.
Loading..........
The Data is Not Available
Activity Intensiveness is defined into Low, where a task typically takes less than an hour, Moderate where a task typically takes approximately a day, or High a tasks typically takes five days.
Customer Assistant means a Generative AI-powered chatbot that interacts with customers.
Efficiency Improvement means the ratio of tasks or activities being processed per employee increases.
External Focus means the task or activity is aimed at a party outside of the financial institution, which could be a customer, a regulator, a professional service provider, or other external parties.
Internal Focus means the task or activity is aimed at another person or function within the financial institution.
ML Model means a traditional Machine Learning model, that typically combines large volumes of numeric data to produce a rank or score, that is used to drive decision-making.
Other AI Tool is an AI-based tool designed to perform a function or task. Other AI Tools are often powered by Generative AI and examples include AI-powered training, AI-based legal tools, AI finance tools, and many more.
Quality Improvement means the output of tasks or activities is improved, for example, fewer mistakes, more insightful analysis or more effective communication.
Team Assistant means a Generative AI-powered chatbot built to support team members with one or more specific functions. Team Assistants are tuned on specific policies, procedures, regulations or other documentation, and they impact functions within the financial institution where large volumes of natural language information are processed, such as Compliance, Legal and Underwriting
(1) University of Oxford
(2) Oliver Wyman
(3) National AI Strategy
https://www.gov.uk/government/publications/national-ai-strategy/national-ai-strategy-html-version
(4) McKinsey
(5) City of London
https://www.theglobalcity.uk/insights/state-of-the-sector-2023
(6) House of Parliament
https://researchbriefings.files.parliament.uk/documents/SN06193/SN06193.pdf

AI is driving growth and efficiencies in Financial Services and Insurance.

Online retailers are improving customer experience and reducing operational overhead with AI tools.